Sapphirine was so named because of its resemblance in color to blue sapphire, even though the two minerals have completely different chemical, optical and physical properties. Sapphirine is very rare, with small gems only faceted for collectors. This gem is know for blue color, but occasionally forms in a red-orange variety.
General Information
Common Name
Sapphirine
Species
Sapphirine
Transparency
Transparent - Translucent
Dispersion
Strength: Moderate Fire Value: 0.019
Refractive Index
1.701-1.734
Birefringence
0.004-0.007
Optic Character
Biaxial
Optic Sign
Positive or Negative
Polariscope Reaction
Aggregate (AGG), Doubly Refractive (DR)
Fluorescence
SWUV: Inert
LWUV: Inert
LWUV: Inert
Pleochroism
Trichroic, strong, varying shades of body color
Hardness
7.5
Streak
White
Specific Gravity
3.400-3.580
Toughness
Fair
Luster
Vitreous
Fracture
Conchoidal
Cleavage
None
Chemical Name
magnesium aluminum silicate
Chemical Formula
(Al,Mg)8(Al,Si)6O20
Crystal System
Monoclinic
Chemistry Classification
Silicate
Sapphirine Colors
-
 Black
Black -
 Blue
Blue -
 Gray
Gray -
 Green
Green -
 Pink
Pink -
 Red
Red -
 White
White -
 Yellow
Yellow
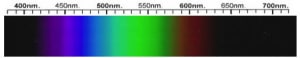
Sapphirine Spectra
We acknowledge the significant scientific contributions of John S Harris, FGA to the study of gemstone spectra and with deep appreciation to him, acknowledges the use of his images and related notes about gemstones and their spectra in the educational materials on this website.
Countries of Origin
Canada; Unknown; Norway; Sri Lanka; United States of America; Italy; Madagascar; France; Greenland
Care
Normal care