What is Luster?
When it comes to describing a gemstone’s appearance, luster refers to
how a gem’s surface looks when it reflects light. Gems and minerals
exhibit a wide range of lusters, from the reflective metallic luster
of polished silver to the entirely non-reflective earthy luster of
clay.
Some minerals can exhibit a wide range of lusters, such as
malachite.
When crystalline, malachite can have a bright adamantine or moderate
vitreous luster. When fibrous it can give a silky appearance and
massive varieties are usually dull or earthy regarding luster.
What gemstone luster is the most common?
The most common luster amongst gemstones is a vitreous luster. This is the luster of most glass and is an easy reference point for determining whether a gem or mineral has a higher or lower luster than vitreous as glass.
Why is luster important?
Luster can be a handy observational property to identify because gemstones with a high luster typically have high refractive indices, and polished gems with lower lusters usually, but not always, have lower refractive indices.
Did you know…? Glittering refers to the luster of the gold, or the quality of the light that is reflected from its surface. Raw gold out of the ground typically has a dull luster that barely reflects at all, compared to its bright metallic luster when polished.
Types of High Luster
The following qualities of luster are typically considered to be higher or brighter in reflective quality than glass:

A highly reflective, often mirrorlike luster
Example Shown: Pyrite

Not quite as reflective as metallic
Example Shown: Gray Hematite

A bright, hard reflective brilliance
Example Shown: Diamond

Brighter than glass, but not quite adamantine
Example Shown: Blue Sapphire

The most common luster among gemstones and the luster of most glass (additives in manmade glass can cause a higher or lower luster)
Example Shown: Rhodolite Garnet
Types of Low Luster
The following qualities of luster are typically considered to be lower or of a less reflective quality than glass:

Similar to mother of pearl, though iridescence may not be
present
Example shown: Shell
Pearl Earrings

A shiny, fibrous quality
Example shown: Tiger’s Eye Beads

A resinous or plastic appearance
Example shown: Amber

Somewhat dull, but still has a slight reflective quality
Example shown: Turquoise

A greasy luster; appears grease or oil coated
Example shown: Brown Opal
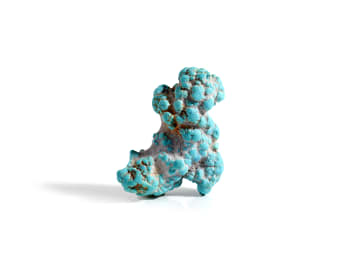
Reflect very little or not at all
Example shown: Unpolished
Turquoise Specimen

Even less reflective than dull, but with a coarser appearance, like
soil
Example shown: Polymer Clay Beads

