Lab created cubic zirconia (CZ) is a popular diamond simulant and is well known in the jewelry industry. Natural cubic zirconia was discovered in 1937 as an inclusion in zircon crystals. The first experiments to synthesize cubic zirconia started in the 1960’s and the process was perfected by 1973. CZ is much harder than many other diamond simulants and has high dispersion making it the most popular affordable diamond simulant. CZ has a higher specific gravity, and will show more abrasion, than a diamond. It is often colorless, but it can be “doped” with various elements to produce a wide array of colors.
General Information
Tolerance:0.03
LWUV: varies with colorcolorless: greenish yellow or yellow-orangetranslucent pink: strong yellow-greentranslucent white: inert
Cubic Zirconia Colors
-
 Bi-color
Bi-color -
 Black
Black -
 Blue
Blue -
 Brown
Brown -
 Colorless
Colorless -
 Gray
Gray -
 Green
Green -
 Multi-color
Multi-color -
 Orange
Orange -
 Pink
Pink -
 Purple
Purple -
 Red
Red -
 White
White -
 Yellow
Yellow
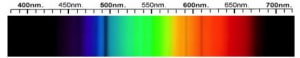
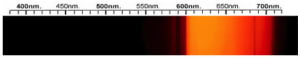
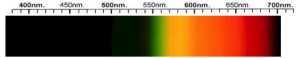
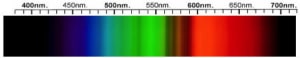
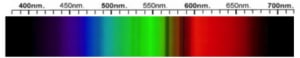
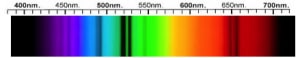
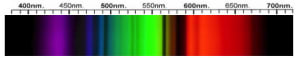
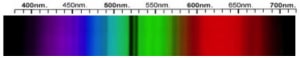
Cubic Zirconia Spectra
We acknowledge the significant scientific contributions of John S Harris, FGA to the study of gemstone spectra and with deep appreciation to him, acknowledges the use of his images and related notes about gemstones and their spectra in the educational materials on this website.
Alternate Names
CZ, Cubic Z, Diamond-Z, Diamonair II, Diamononesque, Diamonite, Djevalite, Phianite, C-Ox, Pearl CZ
Countries of Origin
Tanzania, United Republic Of; Russian Federation; Czechia; Sri Lanka; United States of America; Thailand; Switzerland; India; Austria; Unknown; China; Namibia; Australia
Care
Normal care for untreated stones. In coated stones color may be affected by polishing, recutting, ultrasonic cleaners, alcohol, and harsh chemicals. Coating can be scratched.