Charoite offers an intriguing, mystical array of patterns that are both eye-catching and mesmerizing. The patterns often exhibit a combination of swirls, veins and spots that give each piece a unique and magical appearance. The name Charoite is used to describe both a mineral and an attractive gem material primarily composed of charoite. The gem material comes from the remote, mountainous region of the Sakha Republic of Russia, which remains its only known source.
General Information
Common Name
Charoite
Species
Charoite
Transparency
Semitranslucent - Opaque
Refractive Index
1.550-1.559
Tolerance:(+0.002/-0.002)
Tolerance:(+0.002/-0.002)
Birefringence
0.009
Optic Character
Biaxial
Optic Sign
Positive
Polariscope Reaction
Aggregate (AGG)
Fluorescence
SWUV: Inert to patchy weak red
LWUV: Inert to patchy weak red
LWUV: Inert to patchy weak red
Pleochroism
Unobservable
Hardness
5-6
Streak
White
Specific Gravity
2.540-2.780 Typical:2.680
Toughness
Fair
Inclusions
Charoite has a fibrous or flame-like appearance with swirls and spots of black, gray, white or brownish orange.
Luster
Vitreous, Waxy
Fracture
Splintery, Granular
Cleavage
Good, in three directions
Chemical Name
hydrated potassium calcium sodium hydroxide fluoride
Chemical Formula
(K,Na)5(Ca,Ba,Sr)8(Si6O15)2Si4O9(OH,F).11H2O
Crystal System
Monoclinic
Chemistry Classification
Rock
Charoite Colors
-
 Purple
Purple -
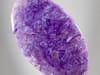 Purple
Purple -
 Purple
Purple
Countries of Origin
Russian Federation; Unknown; China; Zambia


